In the world of finance, arbitrage is the practice of taking advantage of a state of imbalance between two or more markets. A person who engages in arbitrage is called an arbitrageur. The arbitrageur exploits the imbalance that is present in the market by making a couple of matching deals in different markets, with the profit being the difference between the market prices. Essentially, the trader is taking advantage of the same currency being priced differently in two different places.
According to economic theory, trading on financial markets is bound by the Efficient Markets Hypothesis, a concept developed by economist Eugene Fama and others from the 1960s onward. It suggests that markets (or more importantly all the active investors and participants in them) will process all available information about asset values and prices efficiently and quickly in such a way that there will be little, if any, room for price discrepancies across markets, and that prices will move quickly toward equilibrium levels.
In theory, identical objects would be the same price in different markets. However, market inefficiencies, usually in communication, result in different prices. Arbitrage takes advantages of these inefficiencies to profit the trader. For example, if a trader can recognizes that a currency can be bought for less in one market and sold for more in another, he is able to make those trades and keep the difference between the two different currency values.
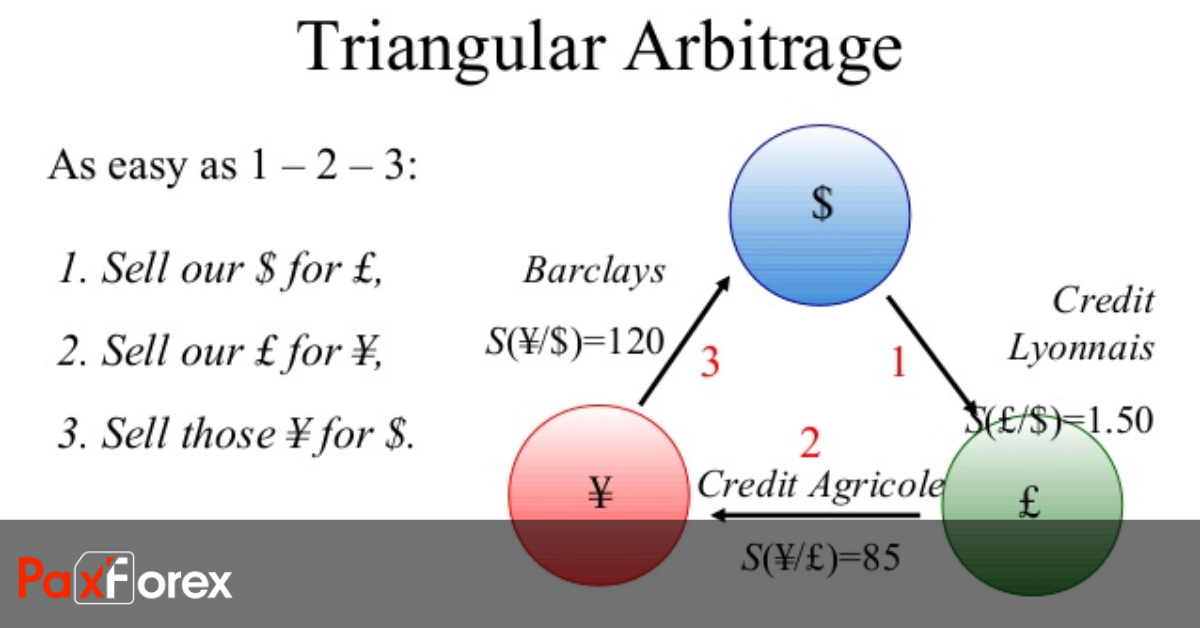
Forex traders take advantage of price differences by buying currencies where they are less valuable and selling them where they are more valuable. In practices this usually involves multiple trades of intermediate currencies. Intermediate currencies are other currencies used to express the value of the currency you are trading. You wouldn't just buy and sell Dollars, for example. You would instead buy Euros with your dollars and sell them for Pounds, which you could then buy dollars with.
Forex arbitrage trading, besides being rare, requires the trader to act quickly as the opportunities disappear just as quickly as they appear. Secondly, most forex brokers tend to use enhanced mechanisms to spot any trades that even remotely look like an arbitrage trade which could result in the profits being deducted. Finally, the currency pair’s spreads also need to be taken into consideration as most arbitrage opportunities that come by usually vary by a few pips only and when the spread is added to the equation, the profits are nearly negligible unless a trader is highly leveraged and well capitalized.







