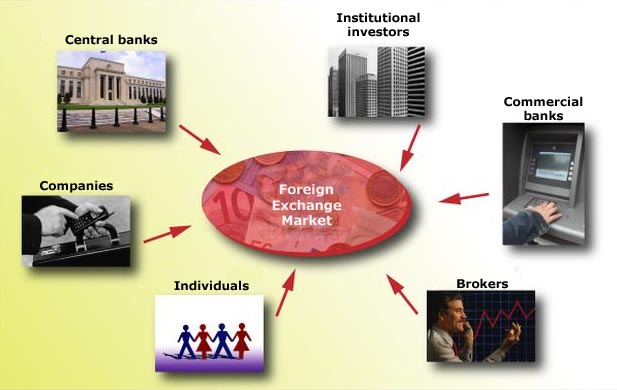
 Foreign currency exchange trading is a fast growing business industry worldwide. The currency exchange takes place on a very large scale and this market has a global presence as currency exchange market participants are from all around the globe. There are various participating entities taking part in forex trading. The main players or the main market participants in currency exchange are Central Banks, largest investment firms, hedge funds, mutual funds and retail forex brokers etc.
Foreign currency exchange trading is a fast growing business industry worldwide. The currency exchange takes place on a very large scale and this market has a global presence as currency exchange market participants are from all around the globe. There are various participating entities taking part in forex trading. The main players or the main market participants in currency exchange are Central Banks, largest investment firms, hedge funds, mutual funds and retail forex brokers etc.
The greatest volume of currency is traded in the interbank market. This is where banks of all sizes trade currency with each other and through electronic networks. Big banks account for a large percentage of total currency volume trades. Banks facilitate forex transactions for clients and conduct speculative trades from their own trading desks. When banks act as dealers for clients, the bid-ask spread represents the bank's profit.
Central banks are extremely important players in the forex market. Open market operations and interest rate policies of central banks influence currency rates to a very large extent. Central banks are responsible for forex fixing. This is the exchange rate regime by which a currency will trade in the open market. Floating, fixed and pegged are the types of exchange rate regimes. Any action taken by a central bank in the forex market is done to stabilize or increase the competitiveness of that nation's economy.
Hedge funds are private investment funds that speculate on the different classes of assets using leverage. Global hedge funds use commercial opportunities in the forex market. They plan and implement transactions based on thorough macroeconomic analysis that reveals challenges to be addressed by a country and its currency. Due to the high trading volumes and aggressive strategies, these funds are the main culprits for the dynamics of the currency market.
The retail market designates transactions made by smaller speculators and investors. These transactions are executed through forex brokers who act as a mediator between the retail market and the interbank market. Individual traders or investors trade forex on their own capital in order to profit from speculation on future exchange rates. They mainly operate through forex platforms that offer tight spreads, immediate execution and highly leveraged margin accounts.







