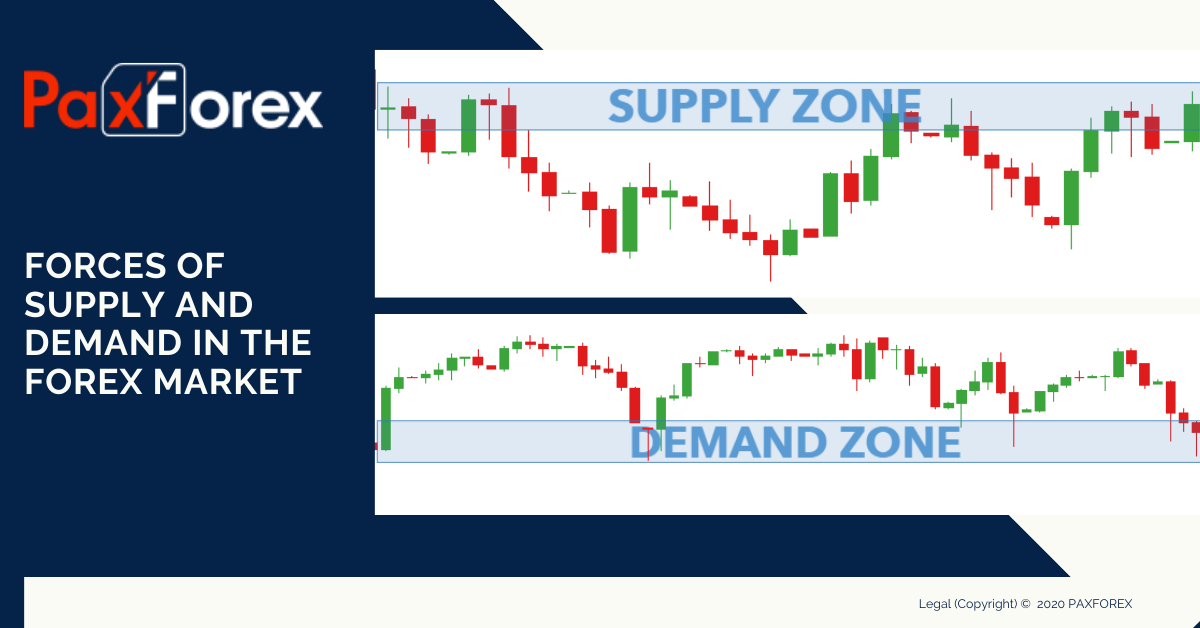
Supply and demand are two factors or forces that affect the forex market. One key to understanding movements in the forex market is to understand the forces affecting supply and demand. Like any market out there, the forces of supply and demand also affect the forex market. Various forces like the business environment, stock market, political factors, and economic data are determinants to the behavior of supply and demand.
Supply and demand is perhaps one of the most fundamental concepts of economics and it is the backbone of a market economy. Demand refers to how much (quantity) of a product or service is desired by buyers. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product people are willing to buy at a certain price; the relationship between price and quantity demanded is known as the demand relationship. Supply represents how much the market can offer. The quantity supplied refers to the amount of a certain good producers are willing to supply when receiving a certain price.
The value of a nation's currency is determined by the supply and demand for that currency. For example, during the 2012 summer Olympics in London tourism to England increased. That could have caused an increase in demand for the British pound and the value of the pound to rise. Generally, exchange rates vary as demand for goods from nations vary. More demand for British goods, for example, would change the demand for the British pound. Just as supply and demand dictate the value of a good, supply and demand will dictate the value of the British pound as well.
Exchange rates and currency supply and demand are very susceptible to the different political factors. Anticipations about new governments and political instability become signals that affect investment. Substantial rises or drops in investments in certain countries become beacons to the exchange rates and also in the forex market. Different events or political conditions in different governments affect the rise and drop in investments.
Different economic data not only reflect the condition of a country's economy it also affects the supply and demand in the currency exchange market. Labor reports such as payrolls, employment/unemployment rates and hourly earnings show productivity in the labor sector. Other items in economic data like Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Producer Price Indices (PPI), International Trade, Consumer Confidence, Productivity, and Consumer Price Indices also affect a country's currency exchange rates and supply and demand.







